Why would you want to poison a rat? That's the first question you should ask yourself here, especially when there are much more effective ways to get rid of a rat infestation from your residential or commercial property.
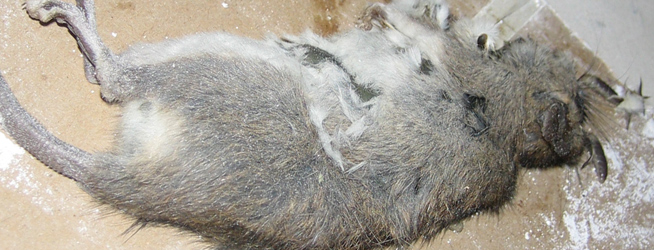
Poison is a bad idea. The average commercially sold poison takes between one and three days to work, for a start, and that's something many homeowners often do not know. Also called rodenticides, they can take as many as three weeks to have the full effect on the rat (death), and many of them use Warfarin, or something similar, in order to work. In case you don't know what Warfarin does, it's a blood thinner. It stops the blood from clotting, and this can cause internal bleeding. In order to cause death to a rat, this would need to happen for a while, and after the first few-day period of the poison taking its time to work, it can then take a further two weeks – 14 days – for that internal bleeding to cause death. In that time, the rat will have crawled somewhere deep inside your home to die, curling up somewhere nice and warm to spend its last few days. You won't know where that place is, but you will soon start to smell the decomposing rat. At that point, you'll have no option but to cut out sections of walls, and pull apart areas of your attic and crawl spaces, in order to find the dead animal.
If the rat has died somewhere that other animals can find it, something called secondary poisoning will then start to occur. This is what happens when another animal, a cat or dog, for example, comes into contact with the dead carcass of the rat. They may play, chew or gnaw on the carcass, thus ingesting the poison that would still be present in the rats body. As you can probably imagine, the poison in the rat can do just as much damage to an animal such as a cat or a dog, even in those low amounts. In fact, it can often be worse, because the symptoms are not pleasant, but you won't have a clue what is causing them. It will only be when you take your beloved pooch or pampered cat to the vet and tests are performed that you'll even realise the animal has been poisoned at all.
That's just the tip of the iceberg too – rat poison can cause even more damage than that. The poison in the rats urine and feces, and also the carcass, can also contaminate water supplies, and also soils and plant matter. Those toxic effects are then exposed to the likes of sick and elderly people, and also children and other animals too. In short, using poisons to get rid of a rat infestation is a very bad idea. Just imagine the kind of amounts of poison you'd be looking at putting down, and the areas of your home too ... Is it worth creating that much damage in the environment around you? Snap traps would be a much quicker, easier, and safer option all-round ... Just so you know.
Go back to the Rats in the Attic home page.
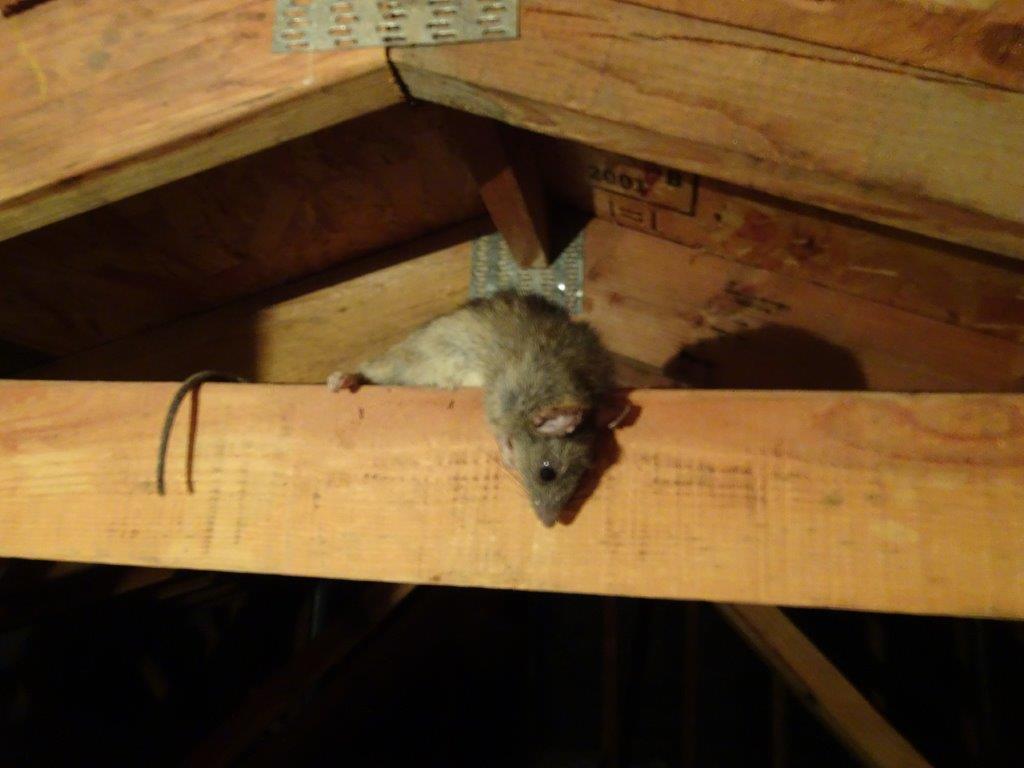

When a rat is spotted or, worst-case scenario, an infestation is found, many people around the country will think poison is the correct solution; after all, don’t professionals use poison?
Many of these products and poisons are prominently displayed in hardware stores and garden centers despite mixed evidence about how effective they actually are, let alone how humane. Even today, many myths exist and people often misbelieve that rats try to escape a property when poisoned, the reality is much worse. Nearly 100% of poisoned rats will die somewhere in your home. This means that you have a decomposing animal somewhere that will certainly attract cadaver flies who will lay eggs and other pests that are attracted to decomposing animals.
Poison will kill a rat, but this isn’t an effective method as only the rat that eats the poison will die. This will lead to a rotting corpse of a rat and the awful stench that will follow. Poisons also act in different ways, depending on the poison used and this can have dire consequences for any person or animal in or around your home.
The common poisons found are as follows:
- Bromethalin - attacks the nervous system and results in seizures, causing a slow and painful death in around 36 hours.
- Strychnine - causes muscular convulsions and then a painful death through asphyxia.
- Anticoagulants - causes blood to thin and eventually stop clotting to cause internal bleeding from tiny injuries to blood vessels. The rat will finally die from shock after a few days.
- Ethylene glycol - causes damage to internal organs resulting in massive organ failure over a period of 24-36 hours.
There are many reasons why poisoning is not a favored way to deal with rats. Some of those reasons are due to the slow and painful death that the rat will suffer. Other reasons are more practical. It isn’t possible to predict exactly where the rat might be when it dies. This means that trying to find the very hazardous corpse can present a lot of problems, and sometimes, rats have been known to die in a location where retrieval isn’t possible without causing structural damage to your home.
Finally, using poison to kill rats can inadvertently poison you, a member of your family, or even a family pet. Poison often remains in the system of a dead and decaying animal and the risk is passed on that anything coming into contact with the dead rat is at risk of secondary poisoning.